lv unloading ecmo | left ventricle effusion ecmo lv unloading ecmo In this large, international, multicenter cohort study of patients with cardiogenic shock treated with VA-ECMO, LV unloading with an Impella was associated with lower mortality, but also . Louis Vuitton handbags which are typically made from Epi leather include the Alma, Holdall, Neverfull, Noe, Speedy and Wallet styles. Types of Epi Leather Keen handbag connoisseurs will note that there are actually 2 types of Epi leather: Classic Epi leather and Electric Epi leather.
0 · venting left ventricle ecmo
1 · venoarterial ecmo venting
2 · venoarterial ecmo unloading criteria
3 · venoarterial ecmo lv unloading
4 · venoarterial ecmo left ventricular pressure
5 · unloading left ventricle ecmo
6 · lv venting ecmo
7 · left ventricle effusion ecmo
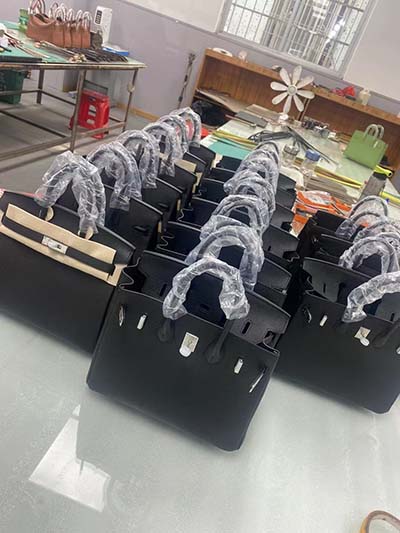
Louis Vuitton's crocodile skins come from farms certified by the Crocodile Standard, a certification launched by LVMH. Louis Vuitton is also one of the last remaining luxury brands to still sell animal fur.
VA-ECMO reduces right atrial pressure, decongesting the liver and kidneys. Mean aortic pressure rises, increasing afterload; if the LV is unable to overcome the increased .In this large, international, multicenter cohort study of patients with cardiogenic shock treated with VA-ECMO, LV unloading with an Impella was associated with lower mortality, but also . In this large, international, multicenter cohort study of patients with cardiogenic shock treated with VA-ECMO, LV unloading with an Impella was associated with lower .
LV mechanical unloading (MU) with intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) or percutaneous ventricular assist device (pVAD) can prevent LV distension, potentially at the risk of more complications, .
venting left ventricle ecmo
LV unloading can be achieved by using an additional circulatory support device to mitigate the adverse effects of mechanical overload that may increase the likelihood of .Based on this analysis, reactive unloading appears to be a viable strategy while venting with the Impella CP provides better than anticipated survival. Our findings correlate with recent large .
LV overload after VA ECMO implantation puts myocardial recovery in danger. Unloading of the LV leads to the reduction in the LV end-diastolic pressure, reduction in the pressure in the left .Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA ECMO) is an established method of short-term mechanical support for patients in cardiogenic shock, but can create left ventricular . VA-ECMO remains an important therapeutic option for patients who are post–cardiac arrest and have refractory cardiogenic shock. Peripheral cannulation for VA .
Background: Left ventricle (LV) unloading during VenoArterial ExtraCorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (VA-ECMO) reduces the risk of LV distention, stagnation and .Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) increases left ventricular (LV) afterload, potentially provoking LV distention and impairing recovery. LV mechanical unloading . VA-ECMO reduces right atrial pressure, decongesting the liver and kidneys. Mean aortic pressure rises, increasing afterload; if the LV is unable to overcome the increased afterload, stroke volume falls, resulting in loss of aortic pulsatility and stagnation of blood, potentiating thrombus formation.
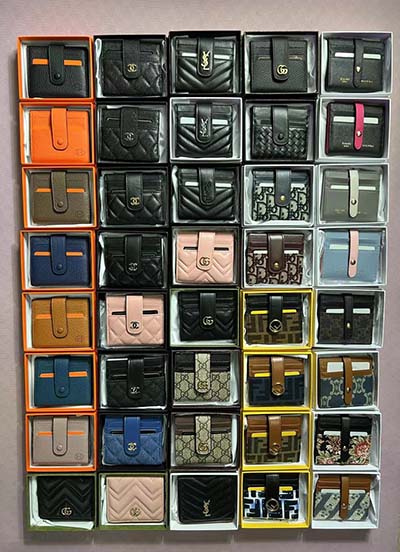
gucci valaintine cake
In this large, international, multicenter cohort study of patients with cardiogenic shock treated with VA-ECMO, LV unloading with an Impella was associated with lower mortality, but also with more bleeding and ischemic complications, compared with VA-ECMO alone.LV mechanical unloading (MU) with intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) or percutaneous ventricular assist device (pVAD) can prevent LV distension, potentially at the risk of more complications, and net clinical benefit remains uncertain.
LV unloading can be achieved by using an additional circulatory support device to mitigate the adverse effects of mechanical overload that may increase the likelihood of myocardial recovery.Based on this analysis, reactive unloading appears to be a viable strategy while venting with the Impella CP provides better than anticipated survival. Our findings correlate with recent large cohort studies and motivate further work to design clinical guidelines and future trial design.
LV overload after VA ECMO implantation puts myocardial recovery in danger. Unloading of the LV leads to the reduction in the LV end-diastolic pressure, reduction in the pressure in the left atrium, and the decrease in the LV thrombus formation risk.Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA ECMO) is an established method of short-term mechanical support for patients in cardiogenic shock, but can create left ventricular (LV) distension. This paper analyzes the physiologic basis of . VA-ECMO remains an important therapeutic option for patients who are post–cardiac arrest and have refractory cardiogenic shock. Peripheral cannulation for VA-ECMO leads to retrograde proximal aortic blood flow that causes increased LV afterload.
Background: Left ventricle (LV) unloading during VenoArterial ExtraCorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (VA-ECMO) reduces the risk of LV distention, stagnation and pulmonary congestion resulting from the increased afterload.Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) increases left ventricular (LV) afterload, potentially provoking LV distention and impairing recovery. LV mechanical unloading (MU) with intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) or percutaneous ventricular assist device (pVAD) can prevent LV distension, potentially at the risk of more . VA-ECMO reduces right atrial pressure, decongesting the liver and kidneys. Mean aortic pressure rises, increasing afterload; if the LV is unable to overcome the increased afterload, stroke volume falls, resulting in loss of aortic pulsatility and stagnation of blood, potentiating thrombus formation. In this large, international, multicenter cohort study of patients with cardiogenic shock treated with VA-ECMO, LV unloading with an Impella was associated with lower mortality, but also with more bleeding and ischemic complications, compared with VA-ECMO alone.
LV mechanical unloading (MU) with intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) or percutaneous ventricular assist device (pVAD) can prevent LV distension, potentially at the risk of more complications, and net clinical benefit remains uncertain. LV unloading can be achieved by using an additional circulatory support device to mitigate the adverse effects of mechanical overload that may increase the likelihood of myocardial recovery.Based on this analysis, reactive unloading appears to be a viable strategy while venting with the Impella CP provides better than anticipated survival. Our findings correlate with recent large cohort studies and motivate further work to design clinical guidelines and future trial design.
LV overload after VA ECMO implantation puts myocardial recovery in danger. Unloading of the LV leads to the reduction in the LV end-diastolic pressure, reduction in the pressure in the left atrium, and the decrease in the LV thrombus formation risk.Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA ECMO) is an established method of short-term mechanical support for patients in cardiogenic shock, but can create left ventricular (LV) distension. This paper analyzes the physiologic basis of . VA-ECMO remains an important therapeutic option for patients who are post–cardiac arrest and have refractory cardiogenic shock. Peripheral cannulation for VA-ECMO leads to retrograde proximal aortic blood flow that causes increased LV afterload. Background: Left ventricle (LV) unloading during VenoArterial ExtraCorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (VA-ECMO) reduces the risk of LV distention, stagnation and pulmonary congestion resulting from the increased afterload.
gucci tumbler with temperature
venoarterial ecmo venting
venoarterial ecmo unloading criteria
gucci trucksuit
In magic, the rule is as long as its the same card (name) you can use any version. Its really cool for some people who like to use printings of cards from like pre 2000 on a standard deck.
lv unloading ecmo|left ventricle effusion ecmo